How To Repair A Shredded Patellar Tendon
Patellar tendon rupture
By Bryson P. Lesniak, MD and Asheesh Bedi, Dr.
Patellar tendon rupture is a rupture of the tendon that connects the patella to the tibia. The patellar tendon is the final extension of the quadriceps musculus in the leg. The 4 muscles that brand up the quadriceps each provide a tendon that attaches to the kneecap (patella). The patella essentially lies inside the quadriceps tendon and is therefore chosen a "sesamoid" bone. The quadriceps tendon becomes thicker and narrower as it travels from the kneecap to the shin bone (tibia). This thicker and somewhat narrower tendon is called the patellar tendon considering it starts at the patella and ends at the tibia.
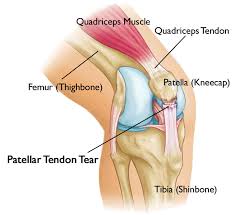
The patellar tendon is instrumental in assuasive a person to straighten his/her leg. When the quadriceps contracts the forcefulness is transmitted through the quadriceps tendon and the patellar tendon, using the patella equally a fulcrum and thus straightening the leg. If any link in this chain is disrupted- whether through aquadriceps tendon ruptureor the patellar tendon rupture, a patella fracture or inability to contract the quadriceps musculus- the leg cannot extend at the knee.Keith Grennan of the Cleveland Browns, Cadillac Williams of the Tampa Bay Buccaneers, Kelenna Azubuike of the Gold State Warriors, and Correll Buckhalter of the Denver Broncos have all suffered from a patellar tendon rupture.
Athletes at take a chance for a patellar tendon rupture
A patellar tendon rupture tends to occur in people historic period 40 and younger. After the gauge age of forty years, the quadriceps tendon becomes the more common tear in the extensor machinery. Whatever condition that affects the quality or integrity of tendons or ligaments increases the gamble of rupture; for example, diabetics and patients who take corticosteroids for an extended period of time for diseases like systemic lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. A growing population at risk is athletes that take anabolic steroids to increment their performance. Steroids can weaken the tendon and increase the risk of its rupture.
Symptoms of Patellar tendon rupture
An athlete that has a patellar tendon rupture has immediate pain and swelling in the knee area. He or she volition oftentimes say they felt a "rip" or "tear" awareness and will be unable to ambulate because of weakness and pain. On examination, in that location are several tell-tale features in improver to pain and swelling in the knee. Get-go, the athlete will be unable to actively straighten the leg. In addition, the examiner tin normally palpate a defect in the tendon below the kneecap. However, in some cases the swelling in the articulatio genus (knee effusion) is severe enough that this is difficult to appreciate. The knee effusion in combination with severe pain with motion often requires radiologic exam to assistance in making the diagnosis.
Patellar tendon tear MRI
Knee X-rays are the showtime imaging studies that are obtained and can be very helpful. When the patellar tendon ruptures, the patella shifts superiorly because of musculus contraction of the quadriceps muscles. This shift in the patella position is called "patella alta." X-rays also evaluate the knee for whatsoever other injuries that can present similarly to a patellar tendon rupture such as a fracture. If whatsoever doubt remains after physical examination and X-rays, an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be performed.
Ultrasonography is a safe, inexpensive and rapid exam that can detect a tendon tear. However, the test is technician dependent and in some facilities is not a reliable diagnostic test. MRI is as well a rubber exam but is more expensive and takes longer to perform. In addition, availability of MRI's can be limited in emergency rooms and a doc'south office. Withal, an MRI tin can also evaluate any other potential bug in the knee such as ligament or cartilage injury.
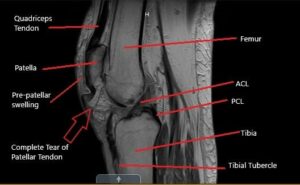
In the vast majority of athletes who have suffered a patellar tendon rupture, an MRI is not indicated as the diagnosis is made with X-rays and physical examination. However, in the instance of partial tears, chronic tears or an unusual presentation, an MRI tin exist a useful diagnostic tool.
Causes patellar tendon rupture
It is mostly accepted that healthy, "normal" patellar tendons do non rupture. That is, in that location is an underlying degeneration in the tendon prior to complete rupture. The usual circumstance surrounding a patellar tendon rupture is when a person suddenly contracts the quadriceps muscle when the knee is in a flexed position. A common example is running upwardly a flight of stairs or when a running backstops running chop-chop to alter direction.
Patellar tendon surgery
For an athlete, patellar tendon surgery is often recommended. If the tear is treated non-operatively, athletes rarely have the ability to extend the leg and ambulate unremarkably without assistance.
Patellar tendon rupture surgery, while not an emergency, should exist performed soon after the injury occurred. This allows for an easier repair before a significant aggregating of scar tissue. Most surgeons perform a directly repair of the tendon if it is torn in the middle. If the tendon is torn off of the os, several different techniques tin exist utilized such as reattaching the tendon to the bone with a combination of sutures and os tunnels. Regardless of technique, the goal of surgical repair is to re-approximate the tendon ends in a secure fashion to allow them to heal.
If the patellar tendon is non repaired soon after the injury (within 5-vi weeks), surgical repair tin become more than hard and accept suboptimal results.
If the tendon cannot be repaired back to itself, a reconstruction tin be performed with a graft from donor tissue (allograft) or tissue taken from some other role of the patient's body (autograft).
Patellar tendon rupture recovery time
Patellar tendon rupture recovery fourth dimension after surgery varies based on surgeon preferences. Later surgery, athletes are placed in a patellar tendon rupturehuman knee brace that keeps their knees direct. Near rehabilitation plans allow initiation of active knee flexion and passive extension past two weeks later on surgery. At 6 weeks later on surgery, athletes can walk without crutches. The stiffness that comes with the patellar tendon recovery, combined with muscle cloudburst creates problems for athletes who need to identify significant load through their knee. And so early on motion combined with early musculus activation is very important. Usually, a return to athletic activities is delayed until 4-six months later surgery based on leg strength and range of motility. The rehabilitation for chronic reconstructions is more substantial and prolonged than above.
Results of surgical repair
If the repair is done acutely (within 3 weeks), most athletes report good or excellent results. About athletes are able to return to their previous level of competition and do not study balance weakness or discomfort. The results with repairs washed afterward three weeks are not equally favorable considering of persistent weakness or poor range of move as the probable cause of disability.
Surgery complications
Loss of knee motility and quadriceps weakness are the two most common bug afterward surgery. Whether this is due to the initial injury or the surgical repair is difficult to decide, only likely due to the initial injury. With postoperative physical therapy as discussed above, the goal is to minimize these issues. Less common complications include persistent genu effusion, infection, and re-rupture of the repaired tendon.
Virtual Care from Sports Doctors and Specialists
 SportsMD offers Virtual Care and Second Opinion Services. It allows you to quickly and conveniently speak with a sports doctor or specialist and have an effective alternative to emergency room, urgent care, or waiting for a doctors date. Yous tin can get Virtual Intendance from your dwelling or anywhere via telephone or video chat.
SportsMD offers Virtual Care and Second Opinion Services. It allows you to quickly and conveniently speak with a sports doctor or specialist and have an effective alternative to emergency room, urgent care, or waiting for a doctors date. Yous tin can get Virtual Intendance from your dwelling or anywhere via telephone or video chat.
Learn more than hither.
References.
1. Siwek CW, Rao JP: Ruptures of the extensor mechanism of the knee joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1981; 63:932-937.
ii. Larsen Eastward, Lund PM: Ruptures of the extensor mechanism of the knee joint: Clinical results and patellofemoral articulation. Clin Orthop 1986; 213: 150-153.
3. Yu JS, Petersilge C, Sartoris DJ: MR imaging of injuries of the extensor machinery of the knee. Radiographics 1994; 14: 541-551.
4. Ecker ML, Lotke PA, Glazer RM: Late reconstruction of the patellar tendon. J Os Articulation Surg Am 1979; 61:884-886.
Source: https://www.sportsmd.com/sports-injuries/knee-injuries/patellar-tendon-rupture/
Posted by: bellephroodession51.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair A Shredded Patellar Tendon"
Post a Comment